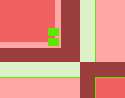
Color Studies
Colors of a complementary relationship.
 Colors of a complementary relationship assigned equal proportion.
Colors of a complementary relationship assigned equal proportion.  Colors reassigned with proportions allocated to dominant and subdominant areas.
Colors reassigned with proportions allocated to dominant and subdominant areas.
 Color intensity and proportion modified. Using tints and shades of the original colors results in a moderate level of contrast and medium value.
Color intensity and proportion modified. Using tints and shades of the original colors results in a moderate level of contrast and medium value.  Colors applied to composition.
Colors applied to composition.
 Color intensity and proportion modified - the whole area displays a moderately-high contrast and medium value.
Color intensity and proportion modified - the whole area displays a moderately-high contrast and medium value.  Colors applied to composition.
Colors applied to composition.
Colors of a triad relationship.
 Colors of a triad relationship assigned equal proportion.
Colors of a triad relationship assigned equal proportion.  Colors reassigned with proportions allocated to dominant, subdominant, and accent areas.
Colors reassigned with proportions allocated to dominant, subdominant, and accent areas.
 Color intensity and saturation modified - the whole area displays a moderately-high contrast level.
Color intensity and saturation modified - the whole area displays a moderately-high contrast level.  Colors applied to composition.
Colors applied to composition.
 Color intensity and saturation modified - the whole area displays a moderately low contrast level.
Color intensity and saturation modified - the whole area displays a moderately low contrast level.  Colors applied to composition.
Colors applied to composition.
 Color intensity and saturation modified - the whole area displays a medium/dark value.
Color intensity and saturation modified - the whole area displays a medium/dark value.  Colors applied to composition.
Colors applied to composition.
 Color intensity and saturation modified - the whole area displays a light value,
Color intensity and saturation modified - the whole area displays a light value,  Colors applied to composition.
Colors applied to composition.


 Moderately-high contrast, medium value, composition using fully saturated hues.
Moderately-high contrast, medium value, composition using fully saturated hues. High contrast, medium value, composition using shades, tints & various saturation levels.
High contrast, medium value, composition using shades, tints & various saturation levels.  Moderately-low contrast, medium-light value, using tints & various saturation levels.
Moderately-low contrast, medium-light value, using tints & various saturation levels. Moderate contrast, medium value, using shades, tints & various saturation levels.
Moderate contrast, medium value, using shades, tints & various saturation levels.  Moderately-low contrast, medium-dark value, using shades & various saturation levels.
Moderately-low contrast, medium-dark value, using shades & various saturation levels. Low contrast, medium value, using shades, tints & various saturation levels.
Low contrast, medium value, using shades, tints & various saturation levels. Moderately-high contrast, medium value, using shades, tints & various saturation levels.
Moderately-high contrast, medium value, using shades, tints & various saturation levels.




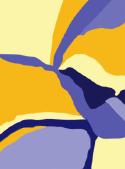

 Dominant color
Dominant color 

 Sub-dominant colors
Sub-dominant colors  Accent
Accent 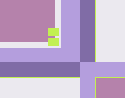
 Dominant color
Dominant color 

 Sub-dominant colors
Sub-dominant colors  Accent
Accent 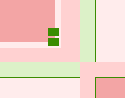
 Dominant color
Dominant color 

 Sub-dominant colors
Sub-dominant colors  Accent
Accent 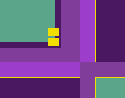
 Dominant color
Dominant color 

 Sub-dominant colors
Sub-dominant colors  Accent
Accent